A Quick Look At PEEK Machining
The use of PEEK polymer for medical implant devices is on the rise. A supplier of this material offers cutting tool tips for shops that may soon add PEEK machining to their list of capabilities.
Share





If you machine components for medical implants, then you’re either 1) already machining PEEK polymer or 2) soon will be. That’s because the medical industry has found medical-grade PEEK offers excellent strength, wear resistance and biocompatibility for components such as the dental healing caps, spiked washers and spinal implants shown in this article. In fact, this material is showing up in an increasing number of medical shops all over the country.
Craig Valentine is the technical manager for Invibio, a UK-based supplier of biocompatible polyetheretherketone (PEEK) polymers. Mr. Valentine provides the following material and machining information for medical shops that may have vast experience machining titanium and stainless, but are just setting their sights on machining this polymer.
Material Differences
PEEK polymer is available in two basic grades: industrial and medical. The industrial-grade is a strong thermoplastic that retains its mechanical properties even at elevated temperatures. The flame-retardant material is abrasion resistant, has high impact strength and a low coefficient of friction. Components made of this material are commonly used in the aerospace, automotive, chemical, electronics, petroleum, and food and beverage industries.
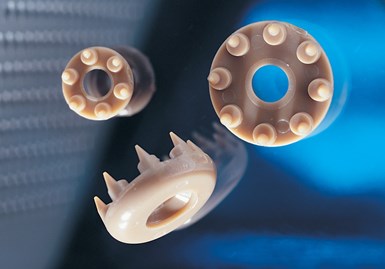
Spiked washers made from PEEK material. Photo: Invibio
Medical-grade PEEK possesses those same physical properties in addition to biocompatibility, high chemical resistance and compatibility with several different sterilization methods. It is also naturally radiotranslucent when viewed using X-ray, MRI or computer tomography (CT). This provides doctors with an unobstructed view of tissue and bone growth around the implant during the healing process. Some such polymers, such as Invibio’s PEEK Classix, are suitable for applications requiring blood or tissue contact of less than 30 days. Others, such as Invibio’s PEEK Optima, have a bone-like stiffness and can remain in contact with blood or tissue indefinitely. Invibio has recently introduced a carbon-fiber-reinforced version, which offers high wear resistance for components such as articulating joints.
Machining Suggestions
Shops typically receive this material in the form of rods that can range from 6 mm to 150 mm in diameter. Before machining, it must be stress-relieved through an annealing process. This decreases the likelihood that heat generated during the cuts will form surface cracks and internal stresses. PEEK components that will undergo long stretches of machining time may require additional intermediate annealing steps. For example, after initial annealing and rough machining, some shops will anneal the workpiece once more before taking finishing passes to prevent crack formation.
Industrial and most medical-grade PEEK polymers are machined similarly. However, medical-grades reinforced with carbon fiber must be approached differently. For instance, this material should be heated just prior to machining in order for it to soften, reducing cutting tool wear. (The table below lists cutting data Invibio offers to help shops dial in their machining processes for conventional medical-grade and carbon-fiber-reinforced PEEK polymers.)

Spinal implants. Photo: Invibio
Invibio also suggests shops use silicon carbide cutting tools for natural PEEK and diamond tools for that which is carbon-fiber-reinforced. The best way to avoid adverse affects on the material’s biocompatibility is to machine dry. However, in many cases coolant is necessary to remove cutting heat that builds in the workpiece (This polymer doesn’t dissipate heat the way metals do.) Pure water serves as the best coolant because it is least likely to affect material biocompatibility. The chips produced from machining most medical-grade PEEK polymers can be collected and recycled for industrial applications.
As with all medical components, precautions must be taken to prevent surface contamination of PEEK workpieces. One precautionary measure is to dedicate the machine tool, fixturing and tools to machining only that material. Some shops also insist their employees use gloves when handling it to keep oils off the part surface.
Related Content
The Producto Group Appoints New Member to Board of Directors
Dean Schauer, the newest appointee to the company’s board of directors, is the current CEO and president of Confluent Medical Technologies.
Read MoreEDM, Laser Micromachining and More at GF Medical Demo Center
At GF’s Medical Center of Competence, the company shows off EDM and laser features that could make a large impact on medical manufacturing — and elsewhere.
Read MoreMikron Milling Tool Suppresses Machining Chatter
IMTS 2024: The CrazyMill Cool CF milling tool features chatter suppression during machining, especially on thin-walled parts, which enables smoother cutting.
Read MoreKennametal Turning Tools Enhance Small Part, Medical Machining
TopSwiss Micro Boring Solid tooling and KCU25B turning inserts are well suited for the small parts and medical machining space.
Read MoreRead Next
Machine Shop MBA
Making Chips and Modern Machine Shop are teaming up for a new podcast series called Machine Shop MBA—designed to help manufacturers measure their success against the industry’s best. Through the lens of the Top Shops benchmarking program, the series explores the KPIs that set high-performing shops apart, from machine utilization and first-pass yield to employee engagement and revenue per employee.
Read MoreAMRs Are Moving Into Manufacturing: 4 Considerations for Implementation
AMRs can provide a flexible, easy-to-use automation platform so long as manufacturers choose a suitable task and prepare their facilities.
Read More





















